Pediatric Neurological Examination
Pertinent general examination
·
Head
and neck
o
Head
circumference microcephaly vs. macrocephaly
o
Fontanelles
open vs. closed, size, fullness
o
Dysmorphisms,
symmetry of head/face
o
Skin
lesions congenital or rashes
o
Cranial
and neck bruits carotid, vertebral, temporal, orbital
·
Cardiovascular
o
Heart
sounds, murmurs
·
Abdominal
o
Hepatosplenomegaly
·
Musculoskeletal
o
Joint
swelling
o
Muscle
bulk
o
Spine
scoliosis, neural tube defects
·
Integument
o
Hair,
skin
Mental status
·
Consciousness
·
Appearance
·
Behaviour,
including abnormal movements
·
Language
o
Expressive
aphasia vs. dysphasia
o
Receptive
·
Orientation
o
Time,
place, person
·
Memory
o
Bibliographical
memory
o
Short-term,
long-term memory
Cranial nerves
·
I
Olfactory nerve
·
II
Optic nerve
o
Pupils,
acuity, colour (red), visual fields, fundoscopy
·
III
Oculomotor nerve
o
Medial
rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus down and out
o
Levator
palpebrae superioris muscle
o
Pupil
constriction in accomodation
·
IV
Trochlear nerve
o
Superior
oblique up and out
·
V
Trigeminal nerve (V1-3)
o
Facial
sensation corneal reflex
o
Motor:
masseter, temporalis,
medial
pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid,
anterior belly digastric, tensor
tympani
·
VI
Abducens nerve
o
Lateral
rectus
·
VII
Facial nerve
o
Muscles
of facial expression
·
VIII
Vestibulocochlear nerve
·
IX
Glossopharyngeal nerve
o
Afferent
portion of gag reflex
o
Sensory
posterior 1/3 of tongue,
tonsils,
pharynx,
middle ear,
carotid body
o
Parasympathetic
fibres to the parotid gland
o
Motor fibres
to stylopharyngeus muscle and the upper
pharyngeal muscles.
·
X
Vagus nerve
o
Muscles
of pharynx/larynx
o
Parasympathetic
innervation of all the organs except the suprarenal glands, from the neck down
to the second segment of the transverse colon
·
XI Accessory
nerve
o
Spinal
accessory sternocleidoid muscle, trapezius muscle
o
Cranial
accessory joins with vagus
·
XII
Hypoglossal nerve
o
Muscles
of the tongue
Motor exam
·
Bulk
o
Compare
left vs. right, distal vs. proximal, upper vs. lower limbs
·
Tone
o
Hypertonia,
hypotonia, spasticity, dystonia
o
Truncal
and limb tone
·
Strength
o
Pronator
drift subtle arm weakness, proprioception
o
Power
gradations:
·
0/5 no muscle activation
·
1/5 ineffective muscle activation
·
2/5 gravity removed
·
3/5 against gravity (3+ slight resistance)
·
4/5 some resistance (4- and 4+ gradations)
·
5/5 full power
o
Common
muscles tested:
·
Deltoid
C5 Axillary n.
·
Biceps C6 Musculocutaneous n.
·
Brachioradialis
C6 Radial n.
·
Triceps C7
Radial n.
·
Ext
Carpi Ulnaris C7 Radial n.
·
Ext
Digitorum C7 Radial n.
·
First
Dorsal Interossious T1 Ulnar n.
·
Abductor
Pollicis Brevis T1 Median n.
·
Psoas L1,2 Lumbosacral Plexus
·
Tibialis
Anterior L4,5 Deep Peroneal n.
·
Ext
Hallucis Longus L5 Deep Peroneal n.
·
Ext
Digitorum Brevis L5 Deep Peroneal n.
·
Gastrocnemius S1 Tibial n.
·
Hamstrings S1
Sciatic n.
·
Reflexes
o
Reflex
gradations:
·
0 absent reflexes
·
1+ diminished reflexes, reinforcement
·
2+ normal reflexes
·
3+ increased reflexes
·
4+ increased reflexes with clonus
o
Common
reflexes tested:
·
Brachioradialis C6
·
Biceps C6
·
Triceps C7
·
Patellar L4
·
Gastroc-soleus S1
o
Plantar
responses:
Babinski Chaddock Oppenheim
![]()
o
Other
reflexes:
Hoffman
o
Abdominal
reflexes
Sensory exam
·
Spinothalamic
- light touch and pin-prick
·
Dorsal
columns - vibration and proprioception
·
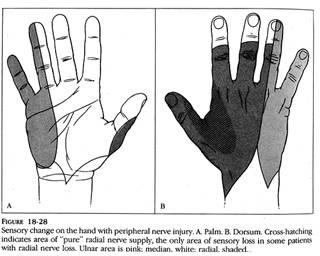
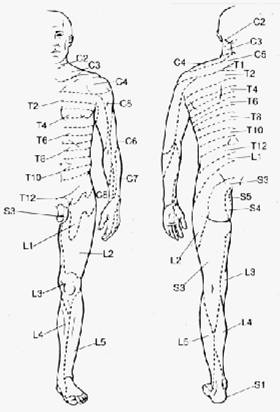
Landmarks:
o
C5 Deltoid area
o
C6 Thumb
o
C7 Index finger
o
C8 Small finger
o
T4-5 Nipple Line
o
T10 Umbilicus
o
L5 Great Toe
o
S1 Lateral Foot
Coordination
·
Dysmetria
finger-to-nose, heel-to-shin
·
Dysdiadochokinesia
rapid alternating movements
·
Influenced
by strength
Gait
·
Regular
gait, running
·
Toe
walking plantar flexion strength
·
Heel
walking dorsiflexion strength
·
Tandem
gait difficulty if wide-based gait